Portfolio of commercial- and clinical-stage assets targeting serious diseases with unmet need with a focus on cardiovascular indications.
Pipeline
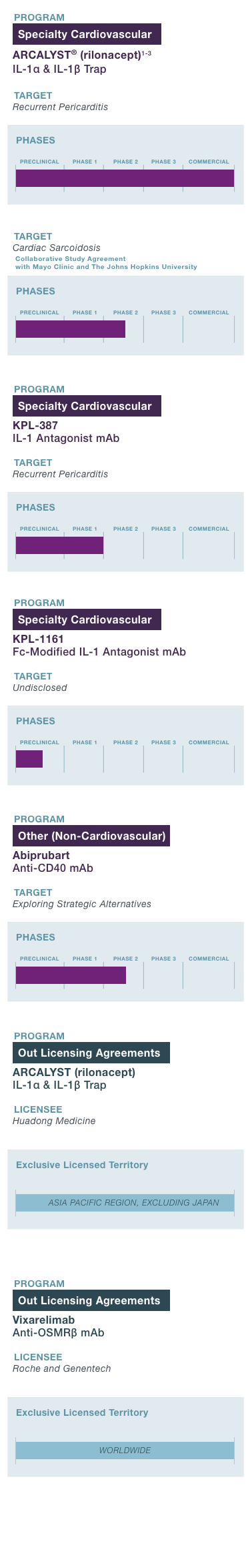
PROGRAM & TARGET
Cardiovascular Franchise
ARCALYST®
(rilonacept)1,2
PHASE: COMMERCIAL
(Excluding MENA)
PROGRAM & TARGET
Cardiovascular Franchise
Mavrilimumab3
PHASE: 1
PROGRAM & TARGET
Autoimmune Franchise
KPL-404
PHASE: 2
OSMRβ
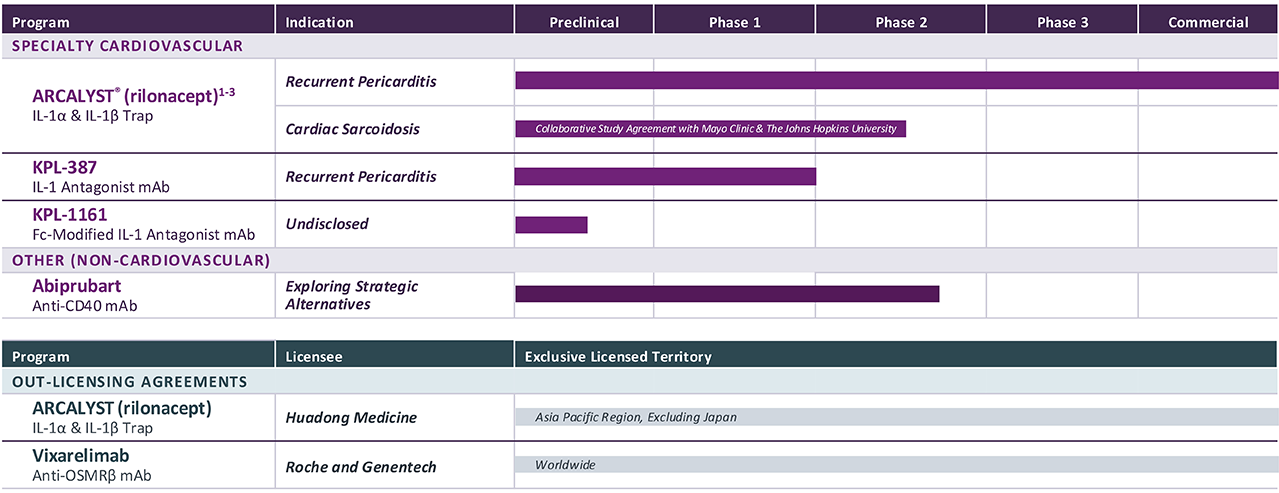
1 Approved in the U.S.; ARCALYST is also approved in the U.S. for cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) and deficiency of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (DIRA);
2 The FDA granted Breakthrough Therapy designation to ARCALYST for recurrent pericarditis in 2019; the FDA granted Orphan Drug exclusivity to ARCALYST in March 2021 for the treatment of recurrent pericarditis and reduction in risk of recurrence in adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older. The European Commission granted Orphan Drug designation to ARCALYST for the treatment of idiopathic pericarditis in 2021;
3 Kiniksa has worldwide rights, excluding the Middle East and North Africa; Kiniksa granted Huadong Medicine exclusive rights in the Asia Pacific Region, excluding Japan.
IL-1α = interleukin-1α; IL-1β = interleukin-1β; IL-1 = interleukin-1; OSMRβ = oncostatin M receptor beta
